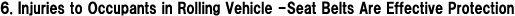
|
The degree of damage to drivers is given in Fig. 15 in terms of vehicle rollover and seat belts. Whether or not a vehicle turns over does not make much difference in the rate of fatality and serious injury for drivers with their seat belt fastened.
Regarding use/non-use of seat belts in vehicle rollover, the fatality rate of drivers fastening their seat belt is 5%, while that of drivers without their seat belt rises to 30%. In other words, for drivers in a rolling vehicle, the risk of fatal accident when the seat belt is not fastened is six times higher compared with when the seat belt is properly used.
|
|
|
|
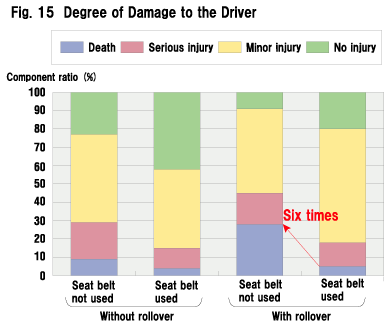
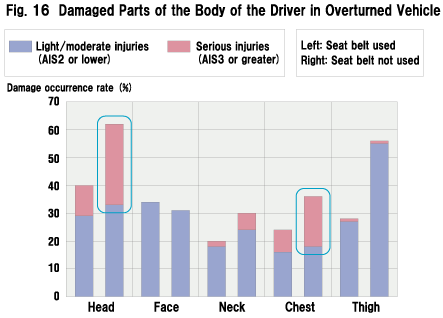
| What is the reason for the high fatality rate of the category "with vehicle rollover/seat belt not used"? Figure 16 shows the parts of the body receiving damage when the driver in an overturned car used/did not use the seat belt. Drivers failing to fasten their seat belt are more subjected to serious head or chest damage. Among those who suffered head injuries in vehicle rollover, drivers not protected by a seat belt mainly fall into the categories "hitting head on the roof" and "thrown out of the car" (Fig. 17).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
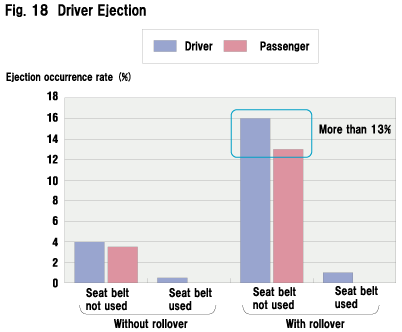
How often are drivers thrown from their vehicles? As shown in Fig. 18, for the drivers and other passengers not fastening their seat belt, the possibility of being thrown from the car is high at 13% or more. On the contrary, only 1% (1 case) of seat-belted occupants are ejected from their vehicles.
In sum, in the case of vehicle rollover, occupants not secured by their seat belts are more likely to be killed by being thrown from their seats and hitting their head severely on the roof or against the road surface or something outside of their car.
|
|
|
|
|
|
UP
Back
|
