 |
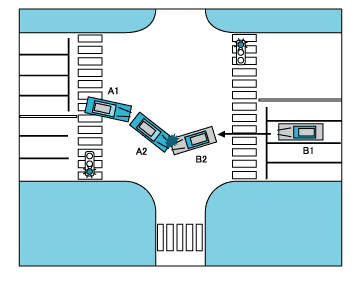
| Figure 12 -- Error of decision-making with Respect to Other Party's Distance and Speed |
|
| Party A |
| 1, |
Drove into intersection on green light and stopped near center of intersection to make a right turn. |
| 2, |
Let several oncoming vehicles pass. |
| 3, |
At a pause in oncoming traffic, perceived no oncoming vehicles and judged it possible to pass.
*Error of decision-making and prediction: Oncoming vehicle faster or slower/panic |
| Party B |
| 1, |
Was aware of Party A up ahead, but judged that he would of course wait and give way.
*Error of decision-making and prediction: Can pass first/mistaken assumption |
| Inferences |
| 1, |
When making a right turn at an intersection, it is easy to rush to conclusions of
decision-making and prediction even when not hurrying. |
| 2, |
Take intersections with deceleration. Do not accelerate, even in error. |
|

